
Play Store Application link – https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.ideepro.java25hours
Get this in action on Youtube-
| Data Type | Primitive/Non-primitive | Description |
|---|---|---|
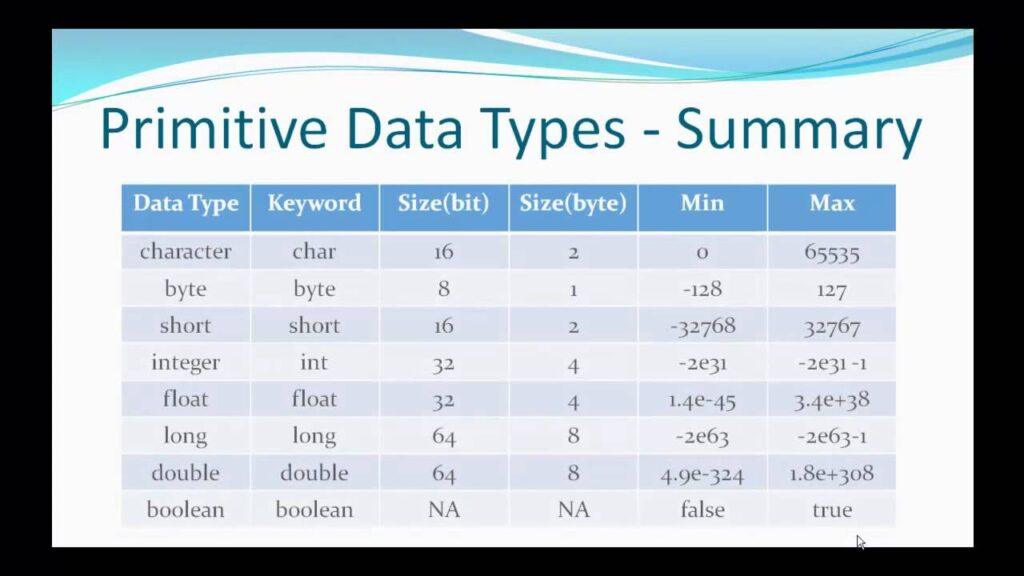
| byte | Primitive | A 8-bit signed integer. Range: -128 to 127. |
| short | Primitive | A 16-bit signed integer. Range: -32,768 to 32,767. |
| int | Primitive | A 32-bit signed integer. Range: -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. |
| long | Primitive | A 64-bit signed integer. Range: -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807. |
| float | Primitive | A single-precision 32-bit floating point. |
| double | Primitive | A double-precision 64-bit floating point. |
| boolean | Primitive | A true or false value. |
| char | Primitive | A single 16-bit Unicode character. Range: 0 to 65,535. |
| String | Non-primitive | A sequence of characters. Non-primitive data type. |
| Array | Non-primitive | A group of variables of the same type. Non-primitive data type. |
| Class | Non-primitive | A template for creating objects. Non-primitive data type. |
| Interface | Non-primitive | A blueprint for a class. Non-primitive data type. |
| Enum | Non-primitive | A special data type that represents a fixed number of predefined constants. Non-primitive data type. |
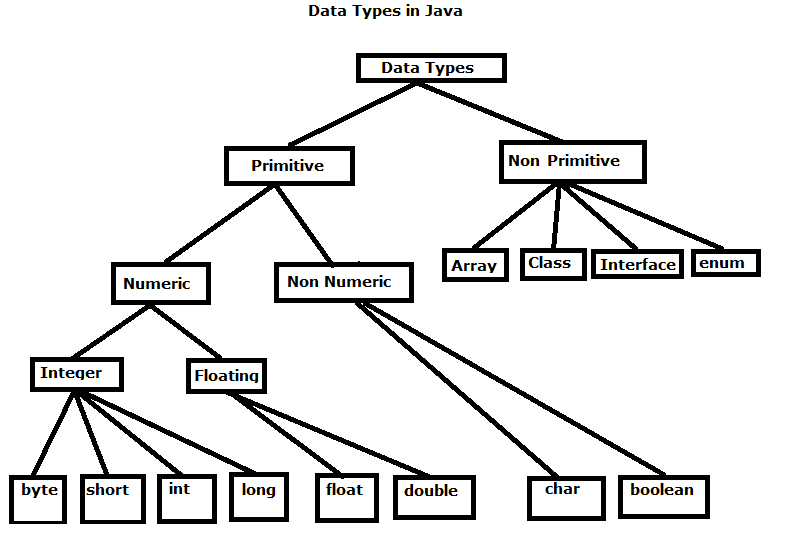
1-Data Types in Java
💡Primitive Data type(predefined)–
💡-int
💡-short
💡-long
💡-float
💡-double
💡-char
💡-byte
💡-boolean
💡Non-Primitive Data type (Referenced/Developer/User defined)-
💡-String
💡-Arrays
💡-Classes
-etc
1-Program to show declaration,instantiation, initialization of all primitive datatypes & non primitive String and then print their values.
declaration-assigning of name
instantiation-assigning memory
initialization-assigning values
package dataype1;
public class Dt {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double d=137.98d;
float f=23.2f;
long l=997511632l;
int i=45;
char v='a';
short s=23;
byte b= 67;
boolean b1=true;
String s6="ngfgdgd  utuytuytb 76575";
System.out.println(d);
System.out.println(f);
System.out.println(l);
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(v);
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(b1);
System.out.println(s6);
}
}
Run this Program ▶️2-Program to print size(in bytes) of all non-primitive datatypes (Using Wrapper classes of primitives datatypes)
package dataype1;
public class Dt1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Double.BYTES);
System.out.println(Float.BYTES);
System.out.println(Long.BYTES);
System.out.println(Integer.BYTES);
System.out.println(Character.BYTES);
System.out.println(Short.BYTES);
System.out.println(Byte.BYTES);
}
}
Run this program▶️3-Program to print size(in bits) of all non-primitive datatypes (Using Wrapper classes of primitives datatypes)
package dataype1;
public class Dt2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Double.SIZE);
System.out.println(Float.SIZE);
System.out.println(Long.SIZE);
System.out.println(Integer.SIZE);
System.out.println(Character.SIZE);
System.out.println(Short.SIZE);
System.out.println(Byte.SIZE);
}
}
Run this program▶️4-Program to print Maximum and Minimum value of all non-primitive datatypes (Using Wrapper classes of primitives datatypes)
Note – Wrapper Classes – Class created with same name as primitive datatype and consists all properties of primitive datatype.
package dataype1;
public class Dt3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Double.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Float.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Long.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Character.MAX_VALUE+0);
System.out.println(Short.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Byte.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Double.MIN_VALUE); //
System.out.println(Float.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println(Long.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println(Character.MIN_VALUE+0);
System.out.println(Short.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println(Byte.MIN_VALUE);
}
}
Run this program▶️ Interview Questions —
- What does primitive mean?
- What is wrapper class?



















**mitolyn**
Mitolyn is a carefully developed, plant-based formula created to help support metabolic efficiency and encourage healthy, lasting weight management.
[…] 4: Classes & Objects – Unlock Java Fundamentals (2nd Hour)Step 5: Java Datatypes Explained – Easy Guide with Code (2nd Hour)Step 6: Java Constructors Explained – Easy Guide with Code (3rd Hour)Step 7: Java Variables […]
Very good tutorial. Easy to understand.