
Play Store Application link – https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.ideepro.java25hours
Learn with youtube video-
💡Types of relationship in classes-
💡1- Is-a relationship-(INHERITANCE)
i.e- class bike, class pulser
Relationship- pulser is a bike
💡2- Has-a relationship-(ASSOCIATION)
i.e- class engine, class pulser
Relationship- pulser has a engine
Overview comparison of inheritance and association in Java:
| Inheritance | Association | |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inheritance is a relationship between two classes where one class (called the subclass or derived class) inherits properties and behavior from another class (called the superclass or base class). | Association is a relationship between two classes where one class has a reference to another class. |
| Syntax | Subclass extends Superclass | Class1 has a reference to Class2 |
| Example | public class Dog extends Animal | public class Dog { private DogHouse house; } |
| Relationship type | “Is-a” relationship | “Has-a” relationship |
| Keyword | extends | N/A |
| Method Overriding | Yes | No |
| Method Overloading | Yes | Yes |
| Multiple Inheritance | No | Yes |
💡INHERITANCE–
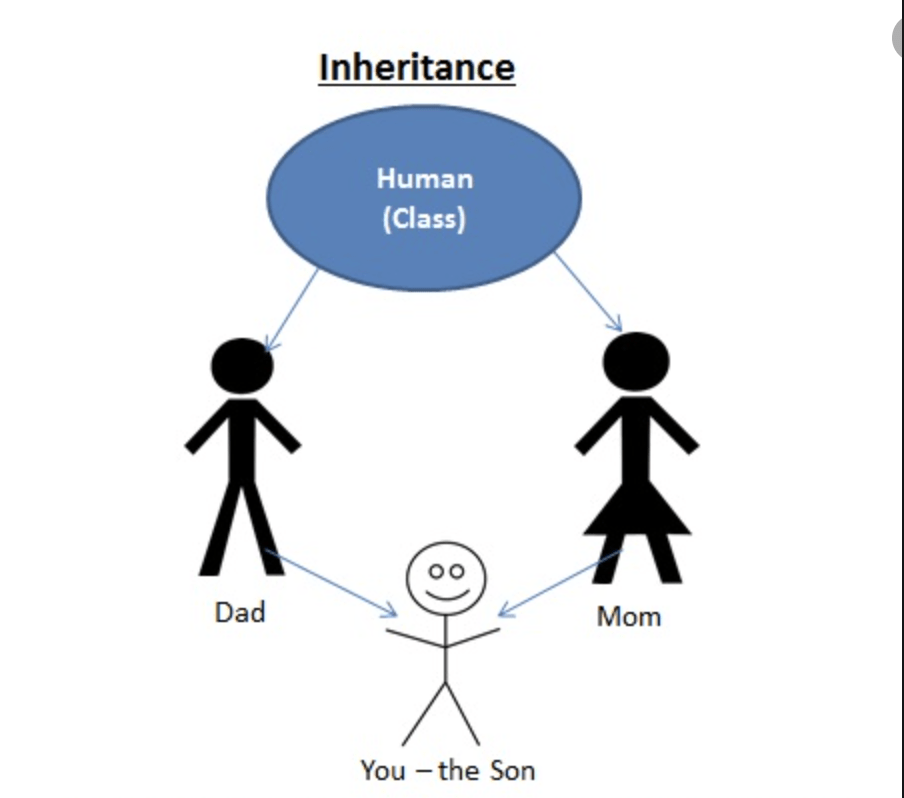
Inheritance is a concept where a class inherits data members and methods from another class.
💡1- Types of inheritance
| Inheritance Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Single Level | Single level inheritance occurs when a subclass extends a superclass. The subclass has access to all of the members of the superclass. | class Animal {...}class Dog extends Animal {...} |
| Multi-Level | Multi-level inheritance occurs when a subclass extends a superclass, and the superclass extends another superclass. The subclass has access to all members of both the superclass and the superclass’s superclass. | class Animal {...}class Dog extends Animal {...}class Poodle extends Dog {...} |
| Multiple | Multiple inheritance occurs when a subclass extends more than one superclass. The subclass has access to all members of all superclasses. | interface A {...}interface B {...}class C implements A, B {...} |
| Hierarchical | Hierarchical inheritance occurs when a superclass has multiple subclasses. Each subclass has access to the members of the superclass. | class Animal {...}class Dog extends Animal {...}class Cat extends Animal {...} |
| Hybrid | Hybrid inheritance is a combination of two or more of the above inheritance types. | – |
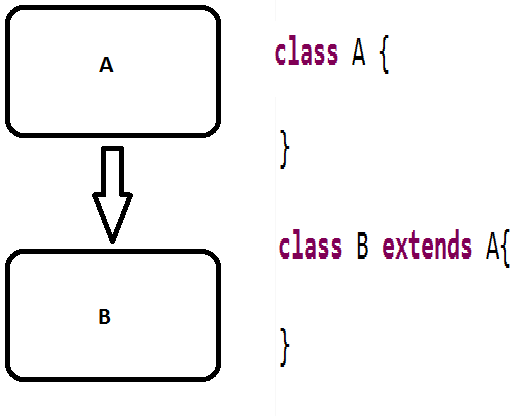
💡(i) Single level inheritance
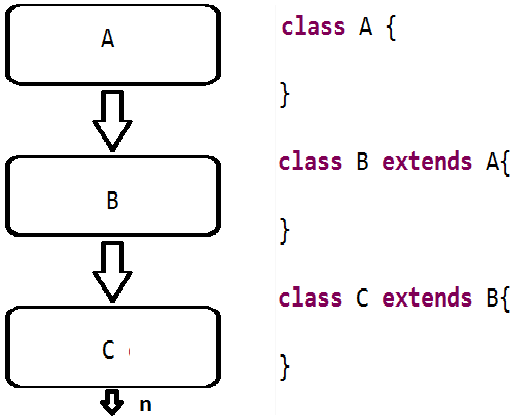
💡(ii) Multi level inheritance
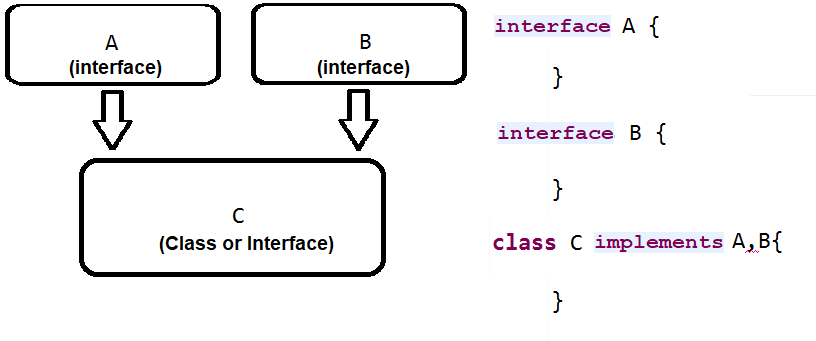
💡(iii)Multiple inheritance

Note – We use interfaces to implement multiple inheritances, and implements keyword is used.
💡(iv) Hierarchical inheritance
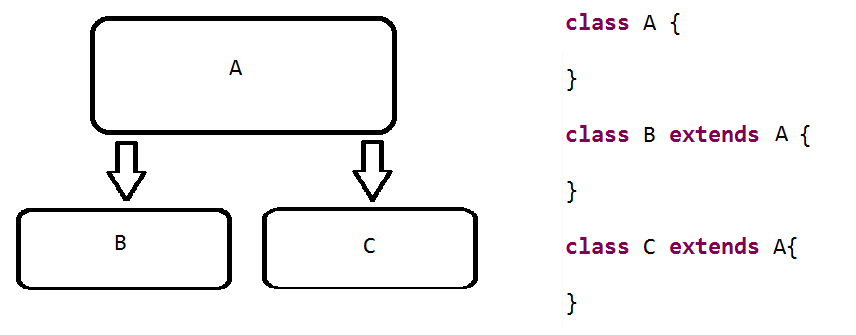
💡(v) Hybrid inheritance –
Combination of any two or more inheritances.
for example –
(1) Single level Inheritance + multiple Inheritance
(2) Multi level Inheritance + multiple Inheritance
(3) Single level Inheritance + hierarchical Inheritance
(4) multi level Inheritance + hierarchical Inheritance
(5) multiple Inheritance + hierarchical Inheritance
💡ASSOCIATION–
Association is a concept where a class has reference of another class.
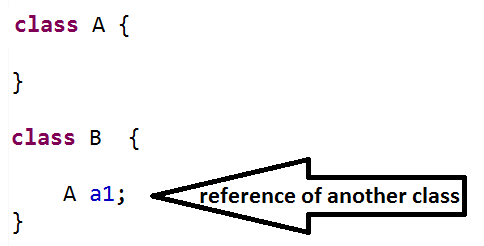
💡2- Types of association
Quick comparison between aggregation and composition in Java:
| Aggregation | Composition |
|---|---|
| Aggregation is a weak relationship between two objects, where one object (the parent) contains the other object (the child). The child object can exist independently of the parent object. | Composition is a strong relationship between two objects, where one object (the parent) contains the other object (the child). The child object cannot exist independently of the parent object. |
| In aggregation, the parent object has a reference to the child object, but it does not own it. | In composition, the parent object owns the child object and is responsible for creating and destroying it. |
| Aggregation is often depicted using a hollow diamond shape on the parent object and a line connecting the parent and child objects. | Composition is often depicted using a filled diamond shape on the parent object and a line connecting the parent and child objects. |
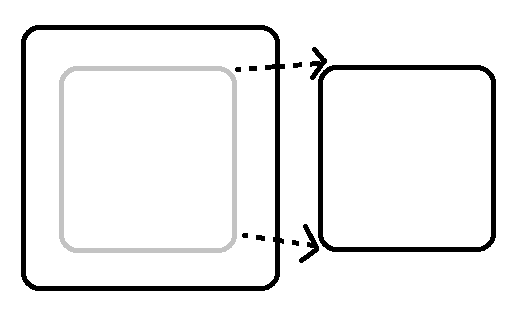
💡(i) Aggregation
-> If we delete parent class, child class will still exist (loose coupled).
public class Organization {
private List<Person> employees;
}
public class Person {
}
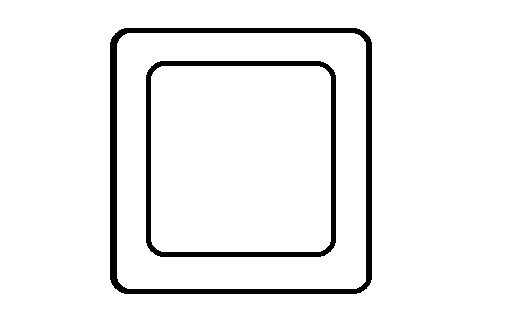
💡(ii) Composition
-> If we delete parent class, child class will also be deleted (tight coupled).
public class Car {
private Engine engine;
public Car(){
engine = new Engine();
}
}
class Engine {
}
code samples are here
1-single level inheritance example- Program to extend class Parent C on class ExampleSingleLevel
package inheritance11;
class ParentC{
String name="paret class variable";
void show(){
System.out.println("Parent class method");
}
}
public class ExampleSingleLevel extends ParentC {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExampleSingleLevel e1=new ExampleSingleLevel();
System.out.println(e1.name);
e1.show();
}
}
2- Multi level inheritance example-
package inheritance11;
class P1{
String a="grandparent variable"; \
void shw(){
System.out.println("grandparent method");
}
}
class P2 extends P1{
String n="parent variable";
void dsplay(){
System.out.println("parent method");
}
}
public class ExampleMultiLevel extends P2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExampleMultiLevel e1=new ExampleMultiLevel();
System.out.println(e1.a);
e1.shw();
System.out.println(e1.n);
e1.dsplay();
}
}
package association12;
public class Engine {
private int engineCapacity;
private int engineSerialNumber;
public Engine(int engineCapacity, int engineSerialNumber) {
this.engineCapacity = engineCapacity;
this.engineSerialNumber = engineSerialNumber;
}
public int getEngineCapacity() {
return engineCapacity;
}
public int getEngineSerialNumber() {
return engineSerialNumber;
}
} b- Class AggregateCar
package association12;
public class AggregateCar {
private String make;
private int year;
private Engine engine;
public AggregateCar(String make, int year, Engine engine) {
this.make = make;
this.year = year;
this.engine = engine;
}
public String getMake() {
return make;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public Engine getEngine() {
return engine;
}
} c- Class Mainclass
package association12;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Engine engine=new Engine(10, 420);
AggregateCar agCar=new AggregateCar("Audi", 2016, engine);
}
} 2- Composition
a- Class Engine-
package association12;
public class Engine {
private int engineCapacity;
private int engineSerialNumber;
public Engine(int engineCapacity, int engineSerialNumber) {
this.engineCapacity = engineCapacity;
this.engineSerialNumber = engineSerialNumber;
}
public int getEngineCapacity() {
return engineCapacity;
}
public int getEngineSerialNumber() {
return engineSerialNumber;
}
} b- Class CompositeCar-
package association12;
public class CompositeCar {
private String make;
private int year;
private Engine engine;
public CompositeCar(String make, int year, int engineCapacity, int engineSerialNumber) { this.make=make;
this.year=year;
engine = new Engine(engineCapacity,engineSerialNumber);
}
public String getMake() { return make; }
public int getYear() { return year; }
public int getEngineSerialNumber() { return engine.getEngineSerialNumber(); }
public int getEngineCapacity() { return engine.getEngineCapacity(); } } c- Class MainClass
package association12;
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Engine engine=new Engine(10, 420);
AggregateCar agCar=new AggregateCar("Audi", 2016, engine);
CompositeCar comCar=new CompositeCar("Ford", 2014, 20, 786);
}
} Interview Questions —
- What is difference between Inheritance and association ?
- Are private methods and private variables are get inherited ?


















